Prostate Cancer Screening
Comprehensive Prostate Cancer Screening
The prostate releases a protein called prostate-specific antigen, or PSA. PSA can be produced by cancerous and non-cancerous cells in the prostate. Small amounts of PSA ordinarily circulate in the bloodstream and can be measured by a PSA test. High levels may indicate the presence of cancer, however many other conditions, such as an enlarged prostate, can also increase PSA levels.
To increase the efficacy of PSA interpretation, we use PSA Density. PSA levels are higher in men with larger prostate glands – PSA density (PSAD) helps adjust for this. Your physician will measure the volume (size) of the prostate gland and then divide your PSA level by the prostate volume.
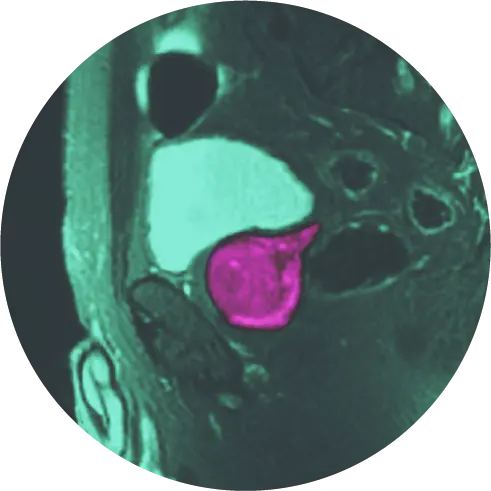
In men with an elevated PSA, the American Urologic Association (AUA) recommends multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) of the prostate prior to a biopsy. A prostate mpMRI can help detect prostate cancer, help determine how advanced the cancer is, and if it has spread to other parts of the body.
A simple urine test, also referred to as a liquid biopsy, such as the ExoDx™ Prostate Cancer Test from ExosomeDx™ (a BioTechne® brand), may also be recommended by your physician. This test is designed to help assess your risk of having clinically significant or high-grade prostate cancer prior to an mpMRI and before biopsy. In fact, this test has been shown to dramatically reduce the number of unnecessary biopsies, especially when paired with a prostate mpMRI. ExoDx may be recommended by your physician when your PSA level is between 2 and 10 ng/mL and you are 50+ years old.


Advanced Screening Program
A recent independent study published by a team of experts at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), indicates combining the ExoDx Prostate Cancer Test with a prostate mpMRI can help identify 100% of clinically significant prostate cancer.1 Give us a call or schedule a consultation to learn more about the advanced screening program offered by HALO Diagnostics.
PSA Test: What is Normal?
PSA tests produce results measured by nanograms of PSA per milliliter of blood (ng/ml).
Most physicians consider a PSA level of 4 ng/ml or higher an indicator that further diagnostics should be performed – a score of 4 ng/ml or above typically means there is a 25% chance that a patient is being diagnosed with prostate cancer. Scores of 10 ng/ml or above typically mean there is a 50% chance of being diagnosed with prostate cancer.
Some doctors will lower the cutoff for further diagnosis to 2.5 or 3 ng/ml, however, doctors largely agree that a score lower than 2.5 ng/ml does not need further examination.
It is important to note that PSA levels can rise naturally with age, and that a number of benign (not cancerous) conditions can also affect PSA levels, such as prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate), benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH, enlarged prostate), urinary tract infection (UTI), or even injury to the prostate. Other factors such as sexual activity right before testing can impact the PSA levels as well, so it is essential to consult a doctor regarding the meaning and next steps of your PSA testing results.
Doctors will frequently ask patients to repeat a PSA test if the first test result was high, to exclude external factors that may be impacting the PSA results.
Learn more about PSA levels and the PSA test here.
Reference: https://www.cancer.gov/types/prostate/psa-fact-sheet
PSA LEVEL < 2.5 ng/ml
Normal
does not need further examination
PSA LEVEL < 4 ng/ml
25% chance
to be diagnosed with prostate cancer
PSA LEVEL < 10 ng/ml
50% chance
to be diagnosed with prostate cancer
WATCH: The inventor of the PSA test, Dr. Richard J. Ablin and his long-time friend, HALO Dx Chief Research Officer, Bernadette Greenwood explain the evolution of the PSA test over the past several decades and the key role it still plays prostate cancer and BPH (benign prostatic hypertrophy) screening today.
The HALO Dx Approach – PSA Density
PSA testing is typically the first step in screening for prostate cancer, however the PSA screening by itself does not indicate if cancer is present.
To increase the efficacy of PSA interpretation, at HALO Dx we use PSA Density instead. PSA levels are higher in men with larger prostate glands. The PSA density (PSAD) adjusts for that. The doctor measures the volume (size) of the prostate gland and divides the PSA number by the prostate volume.
Where Can I Get PSA Testing?
Consult with your general practitioner or urologist about receiving a PSA test in their offices. PSA tests are typically covered by Medicare once a year for men 50 years and older, and there is no co-pay or deductible needed. However, additional PSA test costs may need to be covered by the patient. Many states now have laws which require private health insurers to cover the costs for PSA testing.
Companies such as ImAware also offer take-home PSA testing kits and telemedicine appointments to discuss PSA results with a physician.
Improved Screening with mpMRI
At HALO Dx, we use multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) combined with PSA density as part of our standard of care for prostate cancer.
The American Urologic Association (AUA) now recommends mpMRI along with a PSA test prior to any biopsy.
mpMRI in prostate cancer screening can help:
- Detect prostate cancer.
- Differentiate between aggressive and slow growing cancers.
- Men avoid an unnecessary biopsy.
If a biopsy is needed, mpMRI can be used to more precisely guide the biopsy, ensuring that sampling is not “blind”—randomly taken from across the gland—which may completely miss the disease.
mpMRI: A Clinically Proven Innovation
mpMRI provides a more holistic view of the prostate compared with more traditional approaches. While only a biopsy can diagnose cancer, mpMRI can assist with the characterization of areas within the gland that may warrant biopsy.
mpMRI uses three different types of images to see inside the prostate gland:
- T1- and T2-weighted imaging which show the anatomy of the gland.
- Diffusion- weighted imaging (DWI) which identifies areas where motion of water molecules is restricted due to cancer tissue.
- Dynamic contrast enhanced imaging (DCE) which uses gadolinium-based contrast to find areas where new blood vessels are growing (cancer cells make their own blood vessels to supply themselves with oxygen and nutrients).
Schedule a Call
Submit this form and we will contact you, usually within 24 hours, to answer your Prostate screening, diagnosis, and treatment questions.
1.de la Calle CM, Fasulo V, Cowan JE, et al. Clinical Utility of 4Kscore®, ExosomeDx™ and Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Early Detection of High Grade Prostate Cancer [published online ahead of print, 2020 Sep 8]. J Urol.